What are Merkle Trees and how do they enable Proof of Reserves?
What are Merkle trees and how do they enable Proof of Reserves? You’ll often hear that some kinds of Proof of Reserves are based on “Merkle trees”. But what are they and how do they even work? Here’s what you need to know, in simple terms. 👇
First, what’s a “hash”?
A hash is a unique, immutable sequence of both numbers and letters, generated by a data set of any length and size. In the context of blockchain, this data set can be infinite.
Through a cryptographic hash function, any new block added to a blockchain is linked to the existing block before it. This hash function generates the transaction data from a block into a unique string of text (called a hash) that cannot be altered without also altering the preceding block's hash value and the entire history of the blockchain.
Therefore, altering any part of the data set will also alter its hash. Once converted, the hash can’t be reverse-engineered to reveal the original source data. This mechanism is what makes blockchains ‘cryptographic’, and the data input more secure against decryption.
The cryptographic hash function allows blockchains to be immutable and tamper-proof because every block is intrinsically tied to the blocks that came before and after it.
A Transaction Hash (Tx Hash) is a unique identifier generated by a cryptocurrency transaction to prove that the transaction was validated and added to the blockchain.
Then what’s a Merkle Tree?
Patented by Ralph Merkle in 1979, a Merkle Tree is a hash ‘tree’.
When you initiate a transaction on a decentralized, peer-to-peer network, any changes to the blockchain must be verified for consistency across all participating networks. Without a transaction hash function, networks must continuously validate all transactions on the blockchain, which would be tremendously inefficient. This is where Merkle’s patented tree gets to work.
In order to explain this complex process down in simple terms, we can use an (oversimplified!) analogy. Say you own an ice cream shop, and you need to calculate January’s profit and loss totals. As you complete the tally of losses (e.g., payroll expenses) and profits (e.g., customer payments) with pen and paper, you notice an input error you made on what you paid for cream and sugar on January 5th.
By altering the payment transaction amount made on January 5th, you now must change all of your ensuing calculations to the end of the month. We can agree that this system is not only daunting, but tremendously inefficient.
To continue the pen and paper analogy, a cryptographic hash function is similar to Excel or an accounting software, in that you can see updates to any numerical input change the totals in real time, without having to change the rest of the balance ledger.
However, instead of altered numerical inputs changing the numerical total, the transaction hash (Tx Hash) is changed to a different randomized sequence to reflect the changes to transactions on the blockchain. This is where we start to see the value of the hash function AKA Merkle Tree.
Similar to a password generator, data is converted into a randomized alpha-numerical sequence (the hash) and linked to the corresponding transaction on the blockchain, creating a hash ‘tree’ or Merkle tree. Merkle trees can quickly verify data transferred between computers in a peer-to-peer network by ensuring blocks sent between peers are received unaltered and undamaged.
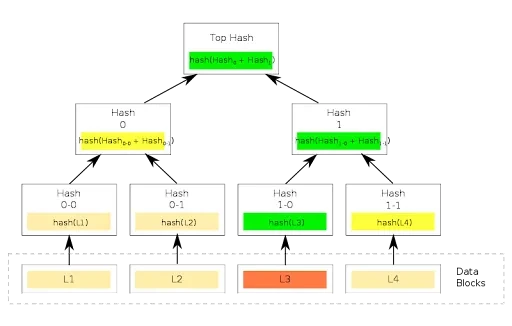
Within crypto, a Merkle Tree consists of leaves or leaf nodes, which are actually the hashes representing blocks of data, such as transactions on a blockchain. Nodes toward the top of the tree are hashes of their respective children.
For example, hash 1 is the combination of the two hashes below it on the tree. I.e., Hash 1 = Hash (hash 1-0 + Hash 1-1).
Sitting at the very top of the tree is what is called the Top Hash (i.e., root). The Top Hash allows any part of the hash tree to be received from any non-trusted source, like a peer-to-peer network.
Then, any received branch, i.e. a new transaction on the blockchain, can be checked against the trusted top hash for verification, to see if the hash is damaged or even falsified by a bad actor.
In other words, instead of sending an entire file over the network, we can just send a hash of the file, and check it against the Top Hash (root) to verify it has not been compromised. Remember, this is partly what defines cryptocurrency as a ‘trustless’ system.
In traditional financial accounting, we use a record system consisting of ledgers, records, and balance sheets, like the earlier example of the ice cream shop. All of the shop’s financial records are reviewed and verified by a third-party auditor. If the auditor finds that the profit and losses don’t add up, they’ll flag it. Only when the discrepancy is resolved will the auditor validate the books.
So what about decentralized exchanges that do not have third party auditors, much less a human balancing incoming and outgoing transactions?
If you sent one ETH to OKX, for instance, how can you tell your deposit is still there, days, months, years later? How can you trust the exchange you use not to use your deposited funds for something else? To you, the balance shown on your screen may not be enough. And it shouldn’t be enough.
There are a number of blockchain explorers out there but history has proved that these aren’t always transparent enough to protect against bad actors. So, what’s a viable, long term solution that actually works for the token holder and not the exchange? Enter the Merkle Tree and Proof of Reserves.
What are Proof of Reserves?
Driven by the desire to alleviate any customer concerns about crypto funds still held in centralized exchanges, OKX launched a Proof of Reserves (PoR) protocol.
Proof of Reserves is a report of crypto assets that ensures the custodian (in this case, OKX) holds the assets it claims to hold on behalf of its users. OKX uses the Merkle tree (hash tree) to prove this claim in two ways:
- First, users can find their balance in the tree and prove their assets are held in the total OKX balance.
- Second, the total OKX balance is compared to the publicized OKX on-chain wallet balance to determine Proof-of Reserves.
Using the Merkle Tree to show immutable transaction data and demonstrate that the data hasn’t been tampered with (through the mechanism of the cryptographic hash), OKX customers can rest assured that their assets are held 1:1.
NOTHING IN THIS ARTICLE IS A SOLICITATION TO BUY OR SELL DIGITAL ASSETS. OKX DOES NOT ENDORSE ANY PARTICULAR DIGITAL ASSET OR STRATEGY. DIGITAL ASSETS HOLDINGS INVOLVE A HIGH DEGREE OF RISK, CAN FLUCTUATE GREATLY ON ANY GIVEN DAY, AND MAY EVEN BECOME WORTHLESS. YOU SHOULD CAREFULLY CONSIDER WHETHER TRADING OR HOLDING DIGITAL CURRENCIES IS SUITABLE FOR YOU IN LIGHT OF YOUR FINANCIAL CONDITION. OKX DOES NOT PROVIDE LEGAL, TAX, INVESTMENT, OR OTHER ADVICE. PLEASE CONSULT YOUR LEGAL/TAX/INVESTMENT PROFESSIONAL FOR QUESTIONS ABOUT YOUR SPECIFIC CIRCUMSTANCES.