Populární témata
#
Bonk Eco continues to show strength amid $USELESS rally
#
Pump.fun to raise $1B token sale, traders speculating on airdrop
#
Boop.Fun leading the way with a new launchpad on Solana.
Mimochodem:
za přibližně 3 týdny Ethereum umožní PeerDAS – novou metodu ukládání dat, která zvýší maximální propustnost sítě až osmkrát!
je to největší zlepšení škálovatelnosti od zavedení Layer-2 rollupů – a výrazné zrychlení směrem k singularitě Etherea
pojďme si co nejjednodušší rozebrat technologii za PeerDAS.
1. jak stále více spotřebitelských aplikací a institucí volí Ethereum kvůli důvěryhodné neutralitě a 100% dostupnosti, objem transakcí dramaticky roste
2. Držet krok s touto poptávkou vyžaduje, aby validátoři instalovali stále větší (a rychlejší) úložiště a šířku pásma – což je stále zvládnutelné, ale postupně nedostupné pro nezávislé validátory, jako jsou home stakery, postupně nedostupné
3. Dvě řešení: opustit domácí stakery, kteří jsou zdrojem decentralizace Etherea (špatné), nebo najít způsoby, jak výrazně zefektivnit ukládání a ověřování transakčních dat, aby domácí stakeři mohli držet krok (dobré)
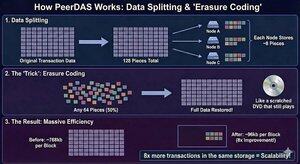
4. představujeme PeerDAS – metodu dělení a distribuce transakčních dat po částech, kde jednotliví validátoři potřebují ověřit a uložit pouze 1/16 původních dat, aby byla plně zachována – obrovské zlepšení efektivity
5. Jak to funguje: místo toho, aby PeerDAS posílal všechna transakční data do každého jednotlivého uzlu v síti, rozdělí je na 128 částí a každému uzlu rozdělí náhodnou sekvenci alespoň 8 částí pro ověření a uložení
6. Síť je poté rozdělena do 128 skupin uzlů – "gossip networks" – z nichž každá je odpovědná za ukládání a ověřování svého vlastního datového prvku. každý uzel patří alespoň do 8 těchto skupin. Společně ukládají všechna data, ale jednotlivě ukládají a zpracovávají výrazně méně, čímž odstraňují omezení zdrojů jako překážku pro zlepšení škálovatelnosti
7. Je to jako rozdělit ověřování a ukládání všech dat na menší části, které lze provádět nezávisle a paralelně, přičemž výsledky pak sloučíte dohromady, čímž se snižuje úsilí každého účastníka
8. Trik je v tom, že pokud bylo >=50 % částí ověřeno a uloženo různými uzly, lze původní data z těchto fragmentů plně obnovit, například poškrábané DVD, které by film stále přehrávalo, pokud by nebylo příliš poškozené.
9. Název tohoto triku je "kódování vymazání". něco jako schválení MultiSIG vyžaduje k/N prah pro odeslání transakce, erasure coding umožňuje rozdělit data na N částí a zvolit prah K, který je potřeba k obnovení původních dat. v PeerDAS je N dílů 128 a k 64 – což je 50% práh
10. Takže zatímco každý uzel se podílí na ověřování a ukládání, síť ve skutečnosti potřebuje jen 50 % dat k obnovení původních, s určitými výhradami. To je dostatečně vysoká překážka, aby odolala koordinovaným útokům na řetězec, a dostatečně nízká, aby umožnila zlepšení efektivity.
11. Mechanicky je u každého bloku minimální počet datových částí, které musí jeden validační uzel stáhnout, uložit a doručit peerům, 8 ze 128
...
Top
Hodnocení
Oblíbené
